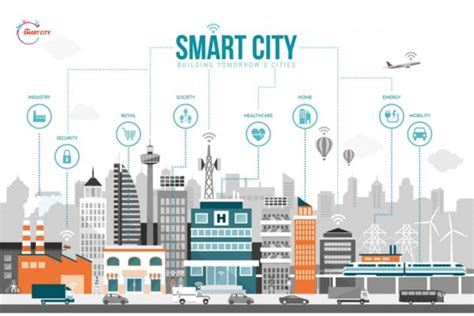
Exploring the emerging trend of Edge Computing in Smart Cities, this introduction sets the stage for a fascinating discussion on how technology is reshaping urban landscapes.
As we delve deeper, we uncover the pivotal role that Edge Computing plays in revolutionizing traditional city infrastructure and paving the way for a smarter, more efficient future.
Overview of Edge Computing in Smart Cities
Edge computing in smart cities refers to the decentralized processing of data closer to the source of generation, such as IoT devices, sensors, and cameras, rather than relying solely on cloud computing.
Edge computing plays a crucial role in enhancing smart city infrastructure by enabling real-time data processing, reducing latency, and improving overall system efficiency. By processing data locally at the edge of the network, smart cities can make quicker decisions, enhance security, and optimize resource allocation.
Differences between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing in Smart Cities
- Edge computing processes data closer to where it is generated, reducing the need to send information back and forth to a centralized cloud server. This minimizes latency and improves response times in smart city applications.
- Cloud computing, on the other hand, relies on centralized servers located in data centers to process and store data. While cloud computing offers scalability and flexibility, it may introduce delays due to the distance data needs to travel.
- Edge computing is especially useful in scenarios where real-time data processing is critical, such as traffic management, public safety surveillance, and emergency response systems in smart cities.
Benefits of Edge Computing in Smart Cities
Edge computing offers several advantages when implemented in smart city projects. One of the key benefits is its ability to improve data processing and reduce latency issues in smart city systems. By processing data closer to the source, at the edge of the network, edge computing minimizes the need to send all data to a centralized cloud server for processing.
This results in faster data analysis and response times, crucial for time-sensitive applications in smart cities.
Enhanced Real-Time Decision-Making
Edge computing plays a pivotal role in enhancing real-time decision-making capabilities in smart cities. By enabling data processing at the edge of the network, near the devices generating the data, edge computing allows for immediate analysis and action based on real-time information.
This leads to quicker responses to changing conditions, such as traffic congestion, environmental changes, or emergencies. With edge computing, smart city systems can make informed decisions swiftly, improving overall efficiency and responsiveness to city-wide events.
Applications of Edge Computing in Smart Cities
Edge computing plays a crucial role in enabling various smart city initiatives by bringing computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. This proximity reduces latency, enhances data processing speed, and improves overall efficiency in delivering smart city services.
Transportation Sector
Edge computing is revolutionizing transportation systems within smart cities by enabling real-time data processing for traffic management, predictive maintenance of vehicles, and autonomous vehicle operations
. For example, edge computing facilitates traffic light optimization, route planning, and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication, leading to smoother traffic flow and reduced congestion.
Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare sector, edge computing supports remote patient monitoring, medical device connectivity, and real-time data analysis for better decision-making. By processing data at the edge, healthcare providers can deliver timely interventions, improve patient outcomes, and optimize resource allocation efficiently.
Energy Management
Edge computing is transforming energy management practices in smart cities by enabling smart grid operations, energy consumption monitoring, and predictive maintenance of equipment. By leveraging edge computing, utilities can balance energy supply and demand, optimize renewable energy integration, and enhance overall grid resilience.
Future Applications
Looking ahead, edge computing is poised to revolutionize smart city technologies further by enabling smart waste management, environmental monitoring, and enhanced public safety systems. With advancements in edge computing capabilities, smart cities can achieve greater sustainability, resilience, and efficiency in delivering services to residents.
Challenges and Considerations of Implementing Edge Computing in Smart Cities
Implementing edge computing in smart cities comes with various challenges and considerations that need to be addressed for successful integration. From security and privacy concerns to scalability issues and regulatory considerations, there are important factors to consider when deploying edge computing solutions in smart city environments.
Security and Privacy Implications
Edge computing in smart cities raises significant security and privacy concerns. With data being processed closer to the source at the edge, there is a higher risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. Ensuring robust security measures, encryption protocols, and data privacy regulations are crucial to safeguard sensitive information and maintain public trust in smart city initiatives.
Scalability Issues
Scalability is a key challenge when implementing edge computing in smart cities. As the volume of data generated by IoT devices and sensors continues to grow, ensuring that edge nodes can efficiently handle the increasing workload becomes essential. Balancing the demand for real-time processing with the capacity of edge infrastructure requires careful planning and investment in scalable solutions.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory considerations play a crucial role in the deployment of edge computing in smart cities. Compliance with data protection laws, privacy regulations, and industry standards is essential to avoid legal implications and maintain ethical practices. Collaboration with regulatory bodies, policymakers, and stakeholders is necessary to navigate the complex legal landscape surrounding smart city technologies.
Epilogue
In conclusion, The Rise of Edge Computing in Smart Cities signifies a paradigm shift in urban development, promising unparalleled advancements in connectivity, efficiency, and sustainability. As we embrace this technological evolution, we embark on a journey towards truly interconnected and intelligent cities.
Questions Often Asked
What are some specific examples of Edge Computing applications in Smart Cities?
Examples include real-time traffic monitoring, smart energy grids, and data analytics for public safety.
How does Edge Computing differ from Cloud Computing in the context of Smart Cities?
Edge Computing processes data closer to the source (at the edge of the network) for faster response times, while Cloud Computing relies on centralized servers.
What challenges are faced when integrating Edge Computing into Smart City infrastructures?
Challenges include ensuring data security, addressing scalability issues, and navigating regulatory considerations.